Balance Sheet Definition & Examples Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This account may or may not be lumped together with the above account, Current Debt. While they may seem similar, the current portion of long-term debt is specifically the portion due within this year of a piece of debt that has a maturity of more than one year. For example, if a company takes on a bank loan to be paid off in 5-years, this account will include the portion of that loan due in the next year. The most liquid of all assets, cash, appears on the first line of the balance sheet. Companies will generally disclose what equivalents it includes in the footnotes to the balance sheet. If a balance sheet doesn’t balance, it’s likely the document was prepared incorrectly.
Company worth

These are also listed on the top because, in case of bankruptcy, these are paid back first before any other funds are given out. Under the accrual basis of accounting, expenses are matched with revenues on the income statement when the expenses expire or title has transferred to the buyer, rather than at the time when expenses are paid. The balance sheet reports the assets, liabilities, and owner’s (stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time, such as December 31. The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position. The accounting equation’s left side represents everything a business has (assets), and the right side shows what a business owes to creditors and owners (liabilities and equity). The shareholders’ equity number is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities.
Balance Sheet
When you use the accounting equation, you can see if you use business funds for your assets or finance them through debt. The accounting equation is also called the balance sheet equation. In short, the balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of what a company owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by shareholders. Balance sheets can be used with other important financial statements to conduct fundamental analysis or calculate financial ratios. The term balance sheet refers to a financial statement that reports a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a specific point in time.
- The main limitation of the Accounting Equation is that it doesn’t tell us anything about the company.
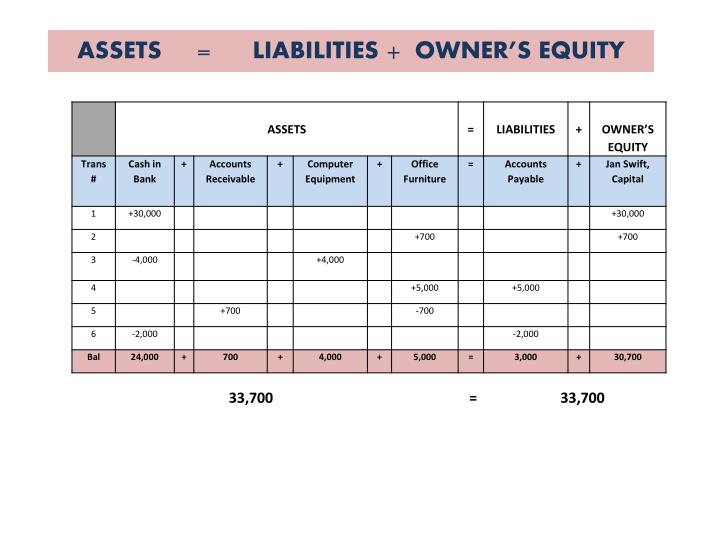
- He funds the venture with $10,000 of his own money and takes out a small business loan for $30,000.
- Balance sheets, like all financial statements, will have minor differences between organizations and industries.
- If the left side of the accounting equation (total assets) increases or decreases, the right side (liabilities and equity) also changes in the same direction to balance the equation.
The accounting equation
A bank statement is often used by parties outside of a company to gauge the company’s health. Employees usually prefer knowing their jobs are secure and that the company they are working for is in good health. That’s because a company has to pay for all the things it owns (assets) by either borrowing money (taking on liabilities) or taking it from investors (issuing shareholder equity). Want to learn more about what’s behind the numbers on financial statements? Explore our eight-week online course Financial Accounting—one of our online finance and accounting courses—to learn the key financial concepts you need to understand business performance and potential. On a more granular level, the fundamentals of financial accounting can shed light on the performance of individual departments, teams, and projects.
A business owns assets and owes liabilities to others and equity to its owners. Every financial transaction recorded reflects movement of economic value from a source to a destination within a closed system. Credits represent the destination on the right side, debits on the left. Everything must be accounted for, and the two sides must be equal. Investors can get a picture of a company’s financial position by examining how the accounting equation relates a business’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity on its financial statements. This basic accounting equation “balances” the company’s balance sheet, showing that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and shareholders’ equity.
Accounting Equation: a Simple Explanation
Whether you’re looking to understand your company’s balance sheet or create one yourself, the information you’ll glean from doing so can help you make better business decisions in the long run. A balance sheet provides mobile bookkeeping and secretarial services a snapshot of a company’s financial performance at a given point in time. This financial statement is used both internally and externally to determine the so-called “book value” of the company, or its overall worth.
Accountants use the Accounting Equation as a guide in their journal entries. It helps them frame how they determine accounts to debit & credit. Every transaction alters the company’s Assets, Liabilities and Equity. It’s the accountants’ responsibilities to keep an accurate journal of these transactions. Every transaction’s impact to Assets must have either offsetting impact to Assets or matching impact to Liabilities and Equity.
Humans are behind all accounting entries and have different points of view, intent, and accounting procedures. Depreciation of an asset can be allocated variably, depending on the point of view of the person assessing the asset. Balance sheets can be “window dressed” by burying losses or pumping profits to present a better financial position. But it has inventory, so you have to reflect that in your balance sheet.
